Rain and flood risk
The risk of flooding in Montpellier is a recurring phenomenon. Discover useful links to protect yourself against these periods of heavy rain.
What is flooding?
Flooding is the more or less rapid submergence of an area due to an increase in the flow of a flooding river, mainly caused by heavy, long-lasting rainfall.
Many factors are involved in the flooding phenomenon:
- rainfall intensity and its distribution in the catchment area
- catchment slope and associated vegetation cover, which contribute to the acceleration or slowing of runoff
- soil absorption and infiltration into the subsoil
- human action of soil sealing, irrigation and deforestation
- snow melt
Consequences: major flooding in valleys and areas close to watercourses; overflowing stormwater systems; flooded, damaged, inaccessible or destroyed homes; disrupted or interrupted communications (power lines, telephone networks, roads) and slowed access for emergency services; burst pipes and problems with drinking water supplies...


Adoptez les bons réflexes
Se préparer avant :
- Informez-vous des risques (réseaux sociaux de la ville ou accueil du site internet),
- Identifiez un espace refuge (mezzanine, étage) accessible de l'intérieur et de l'extérieur,
- Prévoyez le stationnement de votre véhicule hors des zones inondables,
- Placez hors de l'eau les objets précieux, documents ou papiers importants, denrées alimentaires et produits dangereux,
- Constituez votre kit d'urgence pour être prêt à évacuer en cas de besoin.
Concernant vos locaux :
- Ne réintégrez votre domicile que si les conditions y sont favorables,
- Aérez et chauffez dès que possible,
- Ne rétablissez l'électricité que si votre installation a été vérifiée par votre fournisseur,
- Si vous sentez une odeur de gaz, sortez et prévenez ensuite les Sapeurs-Pompiers (18),
- Faites l'inventaire de vos dommages et préparez vos dossiers d'assurance.
Flood risk in Montpellier

The city of Montpellier is subject to a Mediterranean climate that has the particularity of wet, relatively mild winters and hot, dry summers with short, localized stormy precipitation. The heaviest and most risky rainfall occurs mainly in late summer and autumn.
This period is susceptible to "Cevenol episodes", which are linked to intense and rapid rainfall, caused by large accumulations of clouds from the Mediterranean against the southern slopes of the Cévennes.
Precipitation can manifest itself as:
- Overflowing watercourses in Montpellier: the Lez, Mosson, Verdansson, Chambéry, Lantissargues, Rieucoulon, Aiguerelles, Lironde, Rondelet, Grammont... (very rapid, intense precipitation over a watershed that can lead to significant changes in river flow) ;
- Rainwater runoff and stagnation (very rapid, linked to insufficient infiltration or drainage capacity of the soil or stormwater network)
- Rising water tables (fairly slow, water saturation of the soil leading to an exceptional rise in the water level of the water table).
Since January 13, 2004, the city has had a Plan de Prévention des Risques d'inondation (PPRi) for the lower Lez and Mosson valleys.
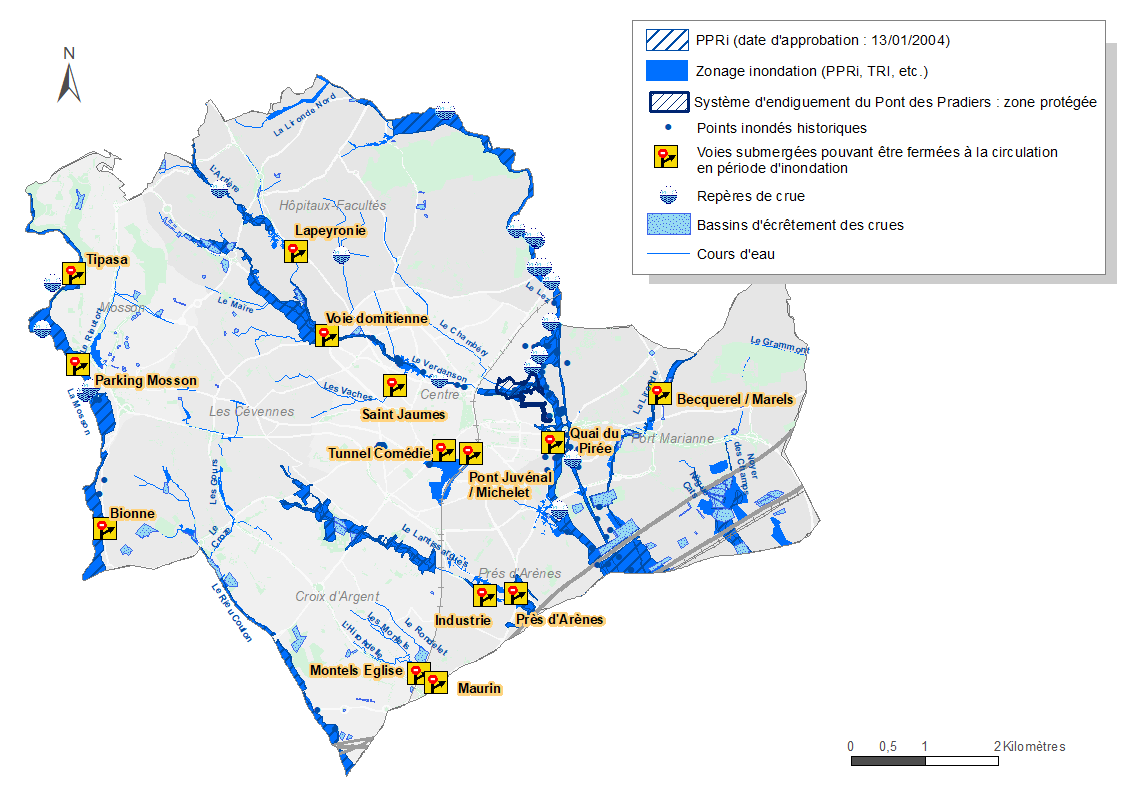
Location of flooded roads
Flood risk prevention policy
It is structured around 5 major, complementary themes:
- Knowledge and inform: for effective prevention, it is important to have a good understanding of the phenomena (particularly based on feedback) and to inform citizens of the risks they face. The development of a culture of risk minimizes the consequences and damage caused by flooding.
- Regulate: the occupation of major riverbeds must be strongly regulated, in particular to prohibit human settlement in the most exposed areas and preserve flood expansion capacities.
- Protect: for areas that are already heavily urbanized, it is possible, in certain cases, to carry out work aimed at reducing risk (flood frequencies and heights) and vulnerability. It may also be possible to slow upstream flows and runoff to reduce the most frequent floods.
- Watch and warn: to reduce the consequences of a flood, it is essential to organize the necessary crisis management operations in advance. You need to be ready to receive the alert and to have programmed the actions required to ensure the safety of people and property.
- A weather watch is provided by the town hall in partnership with the Météo France departmental station. Depending on the level of risk, it can be used to alert the various parties involved and lead to the setting up of a municipal crisis unit.
As soon as an alert is issued, a communal organization is set up through the Plan Communal de Sauvegarde (PCS).
Pluviometric and hydrometric sensors, coupled with the flood warning system of the Service de Prévision des Crues (SPC) Méditerranée Ouest, provide monitoring to anticipate flooding linked to river overflows and to implement appropriate safeguard actions to protect and support populations :
- informing the public about the event and the safety instructions to be followed
- closing flood-prone or submersible roads
- evacuating sensitive buildings and populations at risk of flooding
- closing green spaces, parks, cemeteries to the public
- potentially stopping events.
Prevention tools
Urban development and the establishment of economic activities in flood-prone areas are the main factors aggravating flooding. The safety of people is ensured by a Plan de Prévention des Risques d'Inondation (PPRi) approved on 13/01/2004.
This document, appended to the Plan Local d'Urbanisme (PLU), defines the mapping of flood-prone areas as well as rules and measures aimed at reducing the territory's vulnerability to flood risk.
